Depression is a common mental health disorder that affects millions of people worldwide. It is characterized by persistent feelings of sadness, hopelessness, and loss of interest in activities that were once enjoyed. Depression can have a significant impact on a person’s quality of life, relationships, and overall well-being. In this article, we will explore the symptoms, causes, and treatment options for depression.
Symptoms of Depression

Depression can manifest differently in different people, but some common symptoms include:
- Persistent feelings of sadness, hopelessness, and emptiness.
- Loss of interest or pleasure in activities once enjoyed.
- Difficulty sleeping or excessive sleeping.
- Loss of energy or feeling fatigued.
- Changes in appetite or weight.
- Feelings of worthlessness or excessive guilt.
- Difficulty concentrating or making decisions.
- Thoughts of death or suicide.
It’s important to note that experiencing one or two of these symptoms does not necessarily mean a person has depression. However, if several of these symptoms persist for more than two weeks, it’s important to seek help from a mental health professional.
Prevalence of Depression
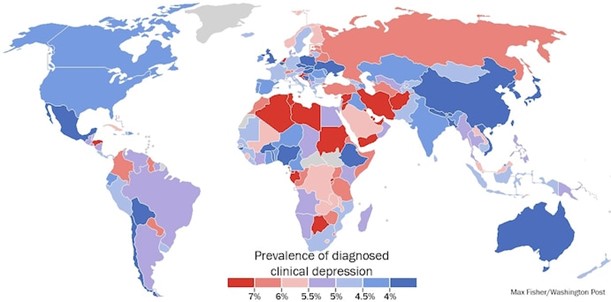
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), over 264 million people globally suffer from depression. In the United States alone, over 19 million adults experience depression in any given year, according to the National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH). Depression can affect people of all ages, genders, and backgrounds, but certain populations may be more vulnerable to the disorder. For example, women are more likely than men to experience depression, and individuals who identify as LGBTQ+ may be at a higher risk of developing depression due to social stigma and discrimination.
Depression is also a leading cause of disability worldwide. In fact, the WHO estimates that depression is the leading cause of disability globally for people aged 15 to 44. Depression can impact a person’s ability to work, socialize, and carry out daily activities, which can have significant economic and social costs.
Another concerning statistic is that suicide is a leading cause of death among individuals with depression. According to the American Foundation for Suicide Prevention, over 50% of individuals who die by suicide have a known mental health condition, with depression being one of the most common.
Despite the prevalence of depression and its impact on individuals and society, many people do not receive adequate treatment for the disorder. According to the NIMH, only about half of individuals with depression receive treatment, and even fewer receive treatment that is considered effective.
Causes of Depression
Depression is complex and can be caused by a variety of factors. Some common causes include:
- Biological Factors: Depression can run in families, indicating a genetic predisposition to the disorder. Chemical imbalances in the brain, such as a decrease in serotonin or dopamine, can also contribute to depression.
- Environmental Factors: Traumatic life events, such as the death of a loved one, a divorce, or a job loss, can trigger depression. Chronic stress and exposure to violence can also contribute to depression.

- Psychological Factors: Negative thought patterns and beliefs, low self-esteem, and a lack of coping skills can contribute to depression.
- Medical Conditions: Chronic pain, thyroid disorders, and other medical conditions can contribute to depression.
It’s important to note that depression can be caused by a combination of these factors, and not everyone who experiences these factors will develop depression.
Treatment Options for Depression
The most common treatments for depression include:
Psychotherapy: Psychotherapy, also known as talk therapy, involves working with a mental health professional to identify and address negative thought patterns and beliefs that contribute to depression. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is a commonly used form of psychotherapy for depression. According to the American Psychological Association, approximately 80% of individuals who receive psychotherapy experience improvement in their symptoms. Different types of psychotherapy, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), interpersonal therapy (IPT), and psychodynamic therapy, can be effective in treating depression.
Medication: Antidepressant medications, such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), can be effective in treating depression by increasing levels of serotonin in the brain. According to the National Institute of Mental Health, approximately 60% of individuals who take antidepressant medications experience improvement in their symptoms. However, it’s important to note that medication may not work for everyone, and it can take several weeks for the medication to take effect.

Exercise: According to the American Psychiatric Association, regular exercise can help reduce symptoms of depression and improve mood. Exercise has been found to increase the production of endorphins, which are chemicals in the brain that help regulate mood. Studies have shown that regular exercise can be as effective as medication in treating mild to moderate depression.

Alternative Therapies: According to a review of studies published in the Journal of Affective Disorders, acupuncture was found to be an effective treatment for depression, with approximately 50% of individuals experiencing improvement in their symptoms. Mindfulness-based therapies, such as meditation and yoga, have also been found to be effective in reducing symptoms of depression and improving overall well-being.
Electroconvulsive Therapy (ECT): ECT involves passing an electric current through the brain to induce a seizure, which can be effective in treating severe depression. However, ECT is generally used as a last resort due to potential side effects.
It’s important to note that treatment for depression may involve a combination of these options and may take time to find the most effective treatment plan for each individual.
Conclusion
Depression is a complex mental health disorder that can have a significant impact on a person’s life. It can be caused by a variety of factors, including biological, environmental, psychological, and medical factors. Fortunately, there are effective treatment options available, including psychotherapy, medication, exercise, and alternative therapies.
It’s important to remember that seeking help for depression is a sign of strength, not weakness. If you or someone you know is experiencing symptoms of depression, it’s important to seek help from a mental health professional. With the right treatment and support, individuals with depression can improve their quality of life and achieve long-term recovery.
References:
American Psychiatric Association. (2013). Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders (5th ed.). Arlington, VA: American Psychiatric Publishing.
Hasin, D. S., Sarvet, A. L., Meyers, J. L., Saha, T. D., Ruan, W. J., Stohl, M., & Grant, B. F. (2018). Epidemiology of adult DSM-5 major depressive disorder and its specifiers in the United States. JAMA Psychiatry, 75(4), 336-346. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2017.4602
Kessler, R. C., Berglund, P., Demler, O., Jin, R., Merikangas, K. R., & Walters, E. E. (2005). Lifetime prevalence and age-of-onset distributions of DSM-IV disorders in the National Comorbidity Survey Replication. Archives of General Psychiatry, 62(6), 593-602. https://doi.org/10.1001/archpsyc.62.6.593
Kupfer, D. J., & Hasler, G. (2012). Neuroscience-based Nomenclature (NbN) for mood disorders: Report and recommendations of a new international society. Brain, 135(8), 2449-2459. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/aws161
National Institute of Mental Health. (2018). Depression. Retrieved from https://www.nimh.nih.gov/health/topics/depression/index.shtml
World Health Organization. (2017). Depression and other common mental disorders: Global health estimates. Retrieved from https://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/254610/WHO-MSD-MER-2017.2-eng.pdf?sequence=1&isAllowed=y

